femoral torsion test|femoral anteversion pediatrics : dealer Femoral Anteversion is a common congenital condition caused by intrauterine positioning which lead to increased anteversion of the femoral neck relative to the femur with compensatory internal rotation of the femur. . WEB25 de jul. de 2019 · Sundhage has reached the last three Olympic Gold Medal matches. The experienced and successful Pia Sundhage has been named the new head coach of the Brazilian women's national team, following the .
{plog:ftitle_list}
* O valor minimo apostado deve ser igual, R$ 2.00. * O valor maximo apostado deve ser igual, R$ 1,000.00. * O valor maximo do prêmio será, R$ 10,000.00.
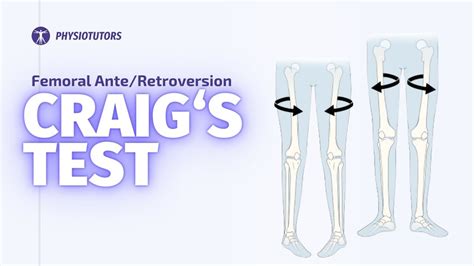
Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence . See more Femoral Anteversion is a common congenital condition caused by intrauterine positioning which lead to increased anteversion of the femoral neck relative to the femur with compensatory internal rotation of the femur. .
Femoral Anteversion test (Craig’s test) Clinical examination Musculoskeletal system Orthopedics. Last modified: Jun 27, 2020. Synonym: Trochanteric prominence angle test. Patient position: Prone with knee on test .
engine compression test procedure pdf
Femoral neck anteversion (FNA) is the angle between the femoral neck and femoral shaft, indicating the degree of torsion of the femur. Differences in FNA affect the biomechanics of the .Craig's Test. Purpose: To determine the anteversion of the femur. Test Position: Prone. Performing the Test: The tested limb's knee is placed in 90 degrees of flexion. The examiner rotates the hip medially and laterally, while palpating the . Femoral anteversion (also called hip anteversion) is when the knee is excessively twisted inward relative to the hip. Learn about diagnosis and treatment. Abnormal femoral antetorsion is associated with the development of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI). Anatomically correct antetorsion measurements are performed on transverse MR images.
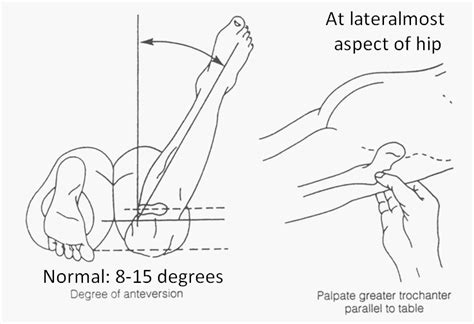
Positive Test: If measures femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. Interpretation: Decreases with age from about 30 0 at birth to about 8 0 to 15 0 at adulthood. .
femoral anteversion test procedure
We evaluated whether the difference in femoral torsion methods increases with increasing femoral torsion. To convert one of the five methods of femoral torsion measurement into .How to Interpret Craig’s Test. Positive Finding: A positive Craig’s test occurs when hip internal rotation is 15˚ or greater, indicating femoral anteversion. Normal hip anteversion is 8 to 15 .
Artificial hip joints must withstand both compressive loads and torsion loads. A minimum of five tests should be run per head/cone type. Before the test, the head and cone must be joined with a specified force analogous to ISO 7206 .Femoral torsion will also cause a change in the angle between the neck of the femur and the femoral condyles. Craig's test: also known as the Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test. Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure .
Femoral antetorsion is the angle between the femoral neck and the femoral condyles and was first described by Julius Wolff in 1868 [1–3].Abnormal femoral antetorsion is associated with slipped capital femoral .
Femoral anteversion (also known as excessive femoral torsion) occurs when a child's thighbone (femur) turns inward. It is often most obvious at about 5 or 6 years of age. The upper end of the thighbone, near the hip, has an increased twist, which allows the hip to turn inward more than it turns outward. This causes both the knees and the feet .Femoral anteversion | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
Positive Test: If measures femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. Interpretation: Decreases with age from about 30 0 at birth to about 8 0 to 15 0 at adulthood. Increased anteversion leads to squinting patellae & pigeon toed .
The femoral head is the top part of the thighbone (femur), the largest bone in the leg. The femoral head may be twisted (called torsion) either internally (the knees point toward each other with toes in, called internal torsion) or externally (the knees point in opposite directions, called external torsion).Purpose: To determine the anteversion of the femur. Test Position: Prone. Performing the Test: The tested limb's knee is placed in 90 degrees of flexion. The examiner rotates the hip medially and laterally, while palpating the greater trochanter area, until the outward most point is found in the lateral aspect of the hip (the greater trochanter is parallel to the table at this point).Femoral osteotomy is a surgical procedure that is performed to correct specific deformities of the femur – the long bone in the upper leg – and the hip joint. Orthopedic surgeons perform the operation, which involves cutting the bone, in order to realign it .
Craig's test is a passive test used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. The examiner palpates the greater trochanter and rotates the hip internally and .Femoral anteversion is an inward twisting of the thigh bone (femur). Femoral anteversion causes a child's knees and feet to turn inward and have a "pigeon-toed" appearance. This is also called in-toeing. Femoral anteversion occurs in up to 10 percent of children. The condition is somewhat more common in girls than boys.
engine compression test range
Femoral anteversion is an inward twisting of the thighbone (femur). The femur is the bone that is located between the hip and the knee. . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean. . Tibial Torsion in Children; Related Topics. Congenital Limb Defect in Children. Femoral Anteversion in Children. Create Personal Test Create Group Test . Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. . and a second line from the lateral to the medial femoral condyles. normal. Abnormal femoral torsion correlates with several disease processes, including hip and knee osteoarthritis, slipped capital femoral epiphysis, trochlear dysplasia with resulting patellar instability, and toe-in or toe-out gait patterns [1, 2].Limb disorders associated with femoral torsion may also be posttraumatic or may be caused by other pathologic conditions, such as . Femoral retroversion occurs when the femoral neck is rotated backward on the femoral shaft. Learn more about the diagnosis and treatment of hip retroversion. . especially if femoral retroversion is combined with a separate rotation deformity such as tibial torsion. Symptoms of femoral retroversion may include: out-toeing or "duck walk .
FEMUR A LA TORSION FEMORAL TOTAL. Fabry en 1973 estableció la definición por todos aceptada del ángulo de anteversión femoral y lo definió como el ángulo que se establece entre dos líneas imaginarias; una trazada a nivel bicondíleo posterior y una segunda línea que unía la cabeza y el cuello femoral.Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance. Less often, the legs turn .
femoral anteversion test criteria
femoral anteversion pediatrics
Find me here: https://linktr.ee/thephysiochannelFREE ONLINE COURSE (for therapists): Mastering Frozen Shoulder: https://daniel-lawrence-fc31.mykajabi.com/off. Femoral retroversion typically improves during the first year of walking. 9 Persistence after three years of age warrants radiography of the pelvis, hips, and lower extremities and referral to an . In the United States, approximately 96% of groin hernias are inguinal hernias, about 20% of which are bilateral. 1 Femoral hernias comprise the remaining 4% of groin hernias and are more common in . Download the FREE Physiotutors App 📲: https://www.physiotutors.com/physiotutors-app/ONLINE COURSES: https://study.physiotutors.comGET OUR ASSESSMENT BOOK ︎.
engine compression test readings
Also known as Craig’s test or trochanteric prominence angle test. Measures amount of femoral torsion.Femoral neck anteversion is the angle between the femoral neck and femoral shaft, indicating the degree of torsion of the femur1. Multiple publications describe the etiology, epidemiology, causalgia, diagnostic imaging, physics/biomechanics, muscle activation implications, and possible musculoskeletal health consequences of anteversion and retroversion. The femoral torsion refers to the twist or torsion between the proximal and distal femur and is typically measured in the transverse plane as the angle between the femur neck axis (FNA) and the posterior condyle line (PCL) of the distal femur . Variations in femoral torsion play an important role in the biomechanics of the hip and knee joint.
Fig. 1A —28-year-old woman with 2-year history of right-sided groin pain and positive anterior impingement test (pain with hip flexion, adduction, and internal rotation). Case emphasizes importance of appropriate imaging workup of patients with suspected femoroacetabular impingement to arrive at correct diagnosis. . Femoral torsion should . Measuring femoral torsion with the trochanteric prominence angle test: With the patient prone, anteversion is measured when the greater trochanteric is palpated in its most prominent position as the hip is internally and externally rotated. When the greater trochanter is most prominent, the femoral neck is horizontal.If the patient’s normal pain is reproduced, the test is considered positive for a SIJ lesion, hip pathology, pubic synthesis instability, or an L4 nerve root lesion. Meanwhile, the femoral nerve may also be stressed by this test. It is recommended to test .
femoral anteversion pdf
WEBWe have over 1,600 lawyers around the world, including nearly 400 partners and other specialists, from technology experts, strategists, to project managers and more.
femoral torsion test|femoral anteversion pediatrics